How Does The Government Influence To Keeping Unemployment Low
There are two principal strategies for reducing unemployment –
- Need side policies to reduce demand-scarce unemployment (unemployment acquired by recession)
- Supply side policies to reduce structural unemployment / (the natural charge per unit of unemployment)
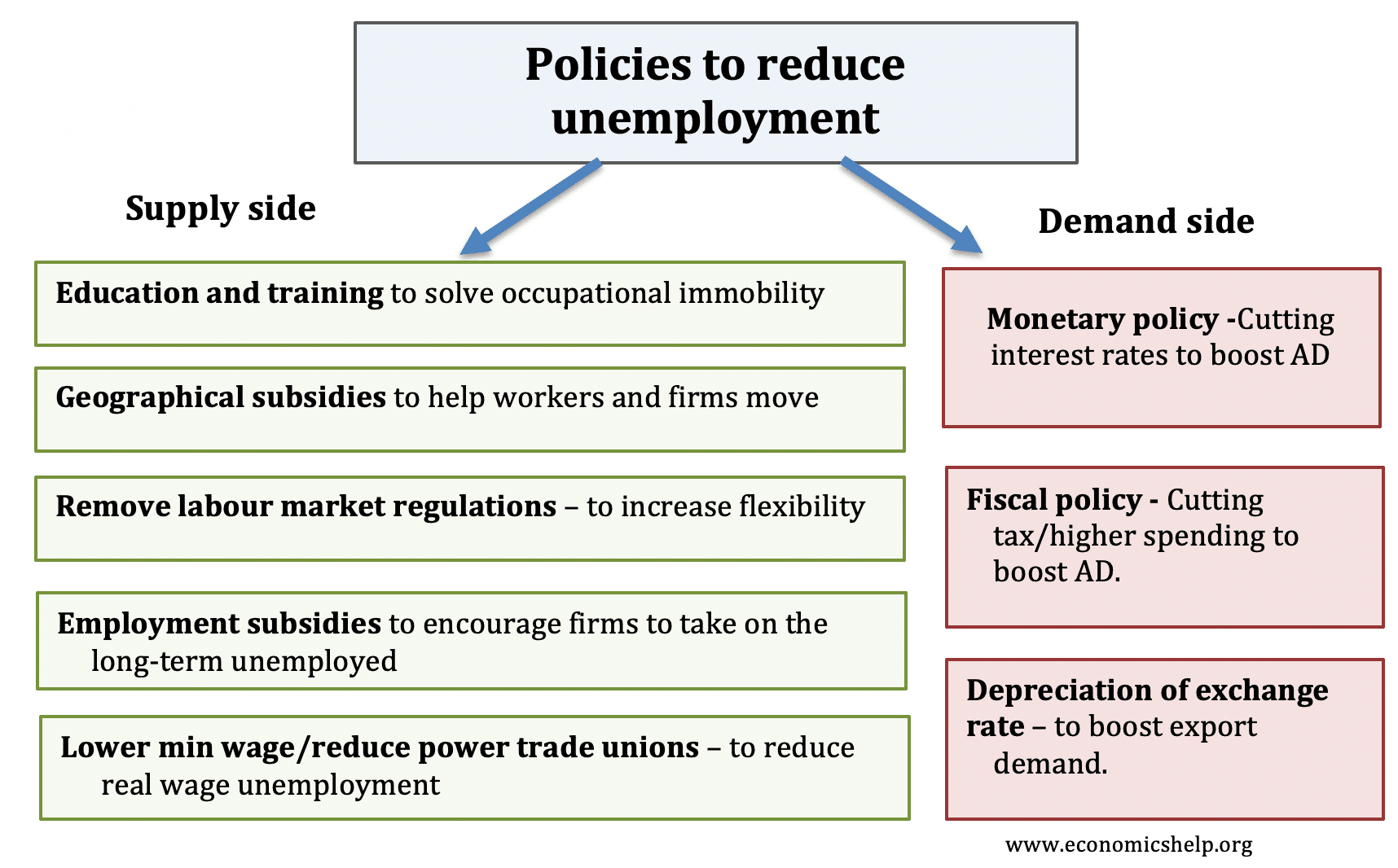
A quick list of policies to reduce unemployment
- Budgetary policy – cutting involvement rates to boost aggregate demand (Advertizing)
- Financial policy – cutting taxes to boost AD.
- Education and training to help reduce structural unemployment.
- Geographical subsidies to encourage firms to invest in depressed areas.
- Lower minimum wage to reduce real wage unemployment.
- More flexible labour markets, to brand it easier to hire and burn down workers.
Video summary
Demand side policies
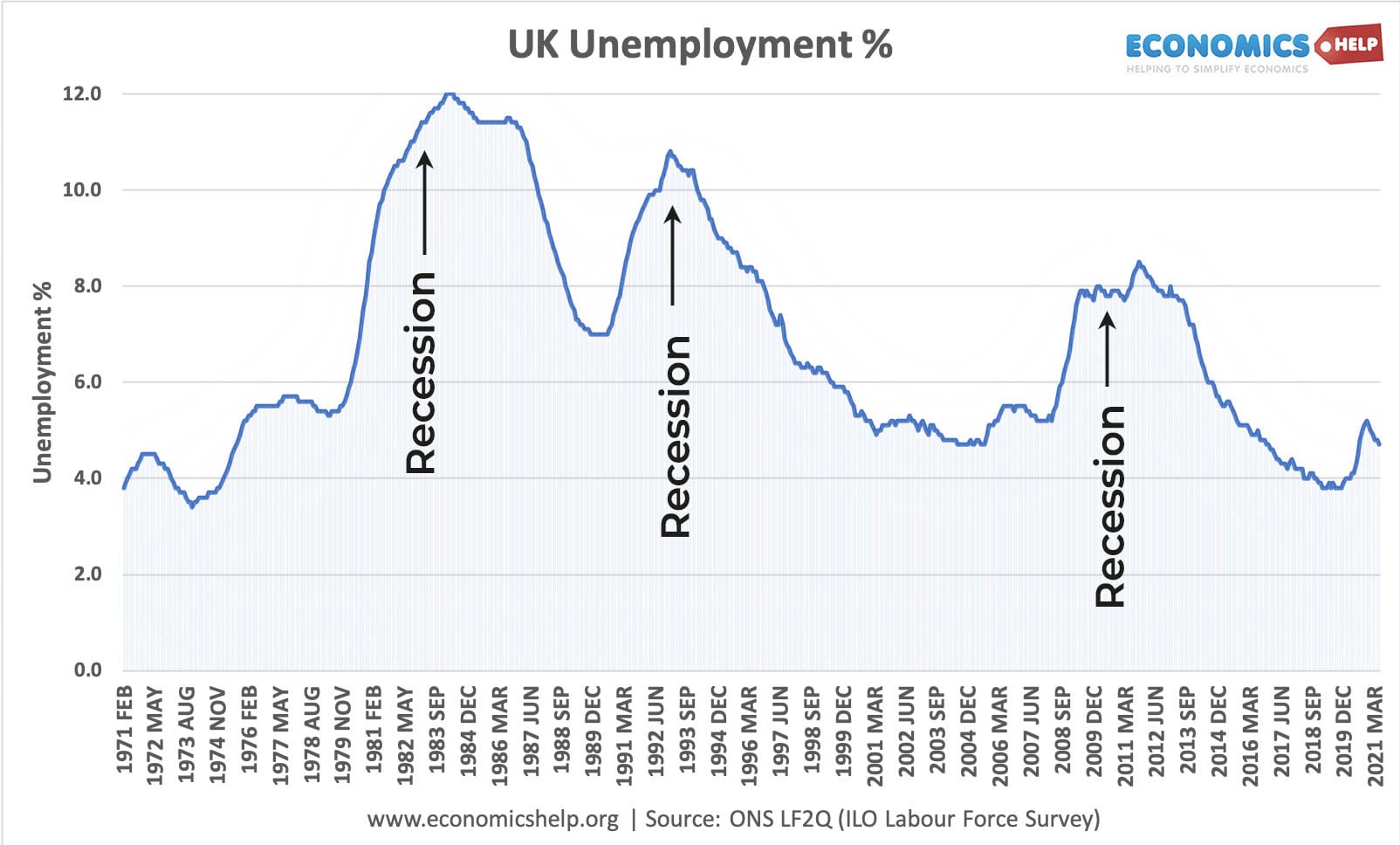
Demand side policies are critical when there is a recession and ascension in cyclical unemployment. (e.chiliad. after 1991/92 recession and later on 2008 recession)
i. Fiscal Policy
Financial policy can subtract unemployment by helping to increment aggregate demand and the charge per unit of economic growth. The government will need to pursue expansionary fiscal policy; this involves cutting taxes and increasing government spending. Lower taxes increase dispensable income (e.g. VAT cutting to 15% in 2008) and therefore help to increase consumption, leading to college amass demand (Advertizing).
With an increase in AD, there volition be an increase in Real Gdp (as long as there is spare capacity in the economy.) If firms produce more, in that location will be an increase in demand for workers and therefore lower need-deficient unemployment. Too, with higher aggregate demand and stiff economical growth, fewer firms will go bankrupt meaning fewer chore losses.
Keynes was an active advocate of expansionary fiscal policy during a prolonged recession. He argues that in a recession, resources (both capital and labour) are idle. Therefore the regime should intervene and create additional demand to reduce unemployment.
Impact of College AD on Economy
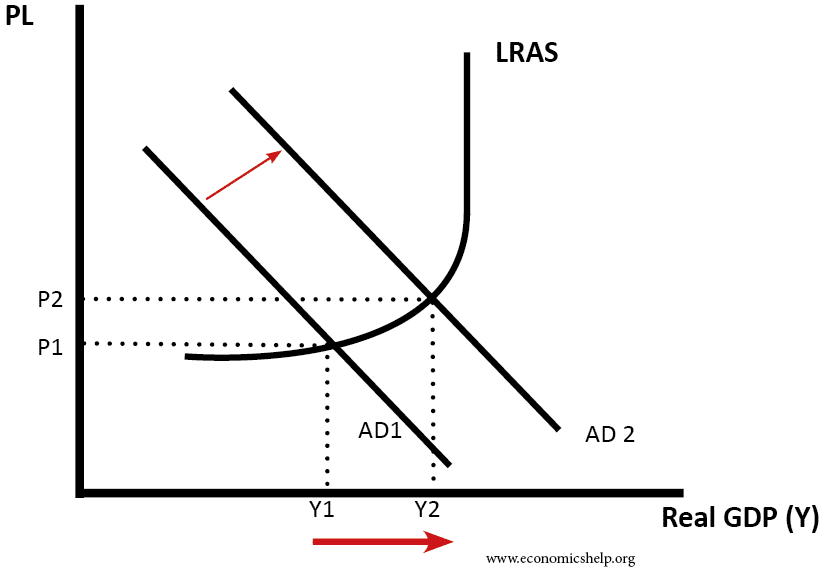
This shows an increment in Advertising causing college existent GDP. The increase in output leads to firms needing more workers.
However,
- Information technology depends on other components of AD. e.1000. if confidence is low, cutting taxes may not increment consumer spending considering people prefer to save. As well, people may not spend revenue enhancement cuts, if they will soon be reversed.
- Fiscal policy may have time lags. E.g., a decision to increment government spending may take a long time to affect aggregated demand (AD).
- If the economic system is shut to full chapters, an increase in AD volition only crusade aggrandizement. Expansionary fiscal policy will merely reduce unemployment if at that place is an output gap.
- Expansionary fiscal policy will require higher government borrowing – this may not be possible for countries with high levels of debt, and rising bond yields.
- In the long run, expansionary fiscal policy may cause crowding out, i.e. the government increment spending simply because they borrow from the private sector, they accept less to spend, and therefore AD doesn't increase. However, Keynesians fence crowding out will not occur in a liquidity trap.
two. Budgetary policy
Budgetary policy would involve cutting interest rates. Lower rates subtract the cost of borrowing and encourage people to spend and invest. This increases Advertizement and should also help to increase Gdp and reduce demand deficient unemployment.
Likewise, lower interest rates will reduce exchange rate and make exports more competitive.
In some cases, lower interest rates may exist ineffective in boosting need. In this instance, Central Banks may resort to Quantitative easing. This is an attempt to increase the money supply and heave amass demand. Run into: Quantitative easing.
Evaluation
- Similar problems to fiscal policy. e.thousand. information technology depends on other components of AD.
- Lower interest rates may non help boost spending if banks are withal reluctant to lend.
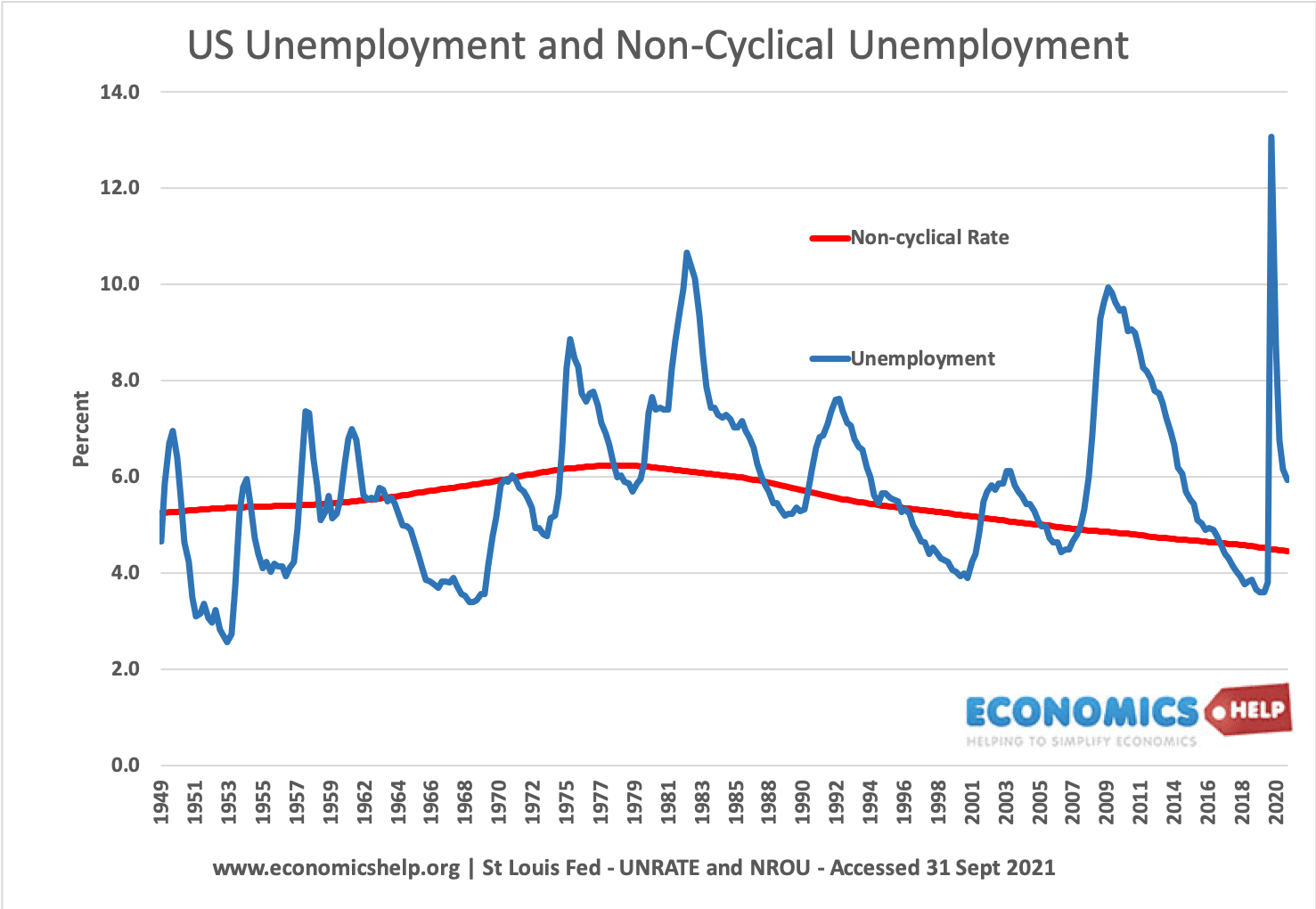
- Demand side policies can contribute to reducing demand deficient unemployment e.g. in a recession. Yet, they cannot reduce supply-side unemployment. Therefore, their effectiveness depends on the type of unemployment that occurs.
Supply side policies for reducing unemployment
Supply side policies deal with more micro-economical issues. They don't aim to boost overall aggregate demand but seek to overcome imperfections in the labour market place and reduce unemployment caused by supply side factors. Supply side unemployment includes:
- Frictional
- Structural
- Classical (existent wage)
Policies to reduce supply-side unemployment
1. Education and training. The aim is to give the long-term unemployed new skills which enable them to observe jobs in developing industries, e.g. retrain unemployed steel workers to take basic I.T. skills which help them detect piece of work in the service sector. – Still, despite providing education and training schemes, the unemployed may exist unable or unwilling to learn new skills. At best it will take several years to reduce unemployment.
ii. Reduce the ability of trades unions. If unions tin deal for wages to a higher place the market clearing level, they will cause real wage unemployment. In this case reducing the influence of trades unions (or reducing Minimum wages) volition help solve this real wage unemployment.
iii. Employment subsidies. Firms could be given tax breaks or subsidies for taking on long-term unemployed. This helps give them new confidence and on the job training. Even so, it will be quite expensive, and it may encourage firms to just replace electric current workers with the long-term unemployment to benefit from the tax breaks.
4. Better labour market flexibility. It is argued that higher structural rates of unemployment in Europe is due to restrictive labour markets which discourage firms from employing workers in the showtime place. For example, abolishing maximum working weeks and making it easier to rent and fire workers may encourage more job creation. However, increased labour marketplace flexibility could cause a rise in temporary employment and greater job insecurity.
5. Stricter benefit requirements. Governments could accept a more pro-active role in making the unemployed accept a job or risk losing benefits. After a certain period, the government could guarantee a public sector task (e.thousand. cleaning streets). This could significantly reduce unemployment. All the same, it may hateful the government end upward employing thousands of people in unproductive tasks which is very expensive. Too, if you make it difficult to merits benefits, you may reduce the claimant count, simply not the International Labour force survey. See: measures of unemployment
6. Improved geographical mobility. Ofttimes unemployed is more concentrated in certain regions. To overcome this geographical unemployment, the government could give revenue enhancement breaks to firms who prepare upwardly in depressed areas. Alternatively, they tin provide financial assistance to unemployed workers who motion to areas with high employment. (eastward.thou. help with renting in London)
7. Maximum working week. It has been suggested a maximum working week of (for example 35 hours) would pb to firms needing to hire more workers and reduce unemployment.
- However, a maximum working calendar week may increase a firms costs and therefore they are not willing to hire more. As well, there is no certainty a house will respond to a cut in hours by employing more – they may endeavor to increment productivity. Those with the wrong skills will yet confront the same trouble.
Video on policies to reduce unemployment
Related
- Causes of Unemployment
- The unemployment problem
- Inflation v Unemployment
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/3881/economics/policies-for-reducing-unemployment/
Posted by: hawkscitine.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Does The Government Influence To Keeping Unemployment Low"
Post a Comment